Selective C–C and C–H Bond Activation/Cleavage of Pinene Derivatives: Synthesis of Enantiopure Cyclohexenone Scaffolds and Mechanistic Insights
Ahmad Masarwa, Manuel Weber, and Richmond Sarpong
J. Am. Chem. Soc.,
2015, 137, (19), 6327; 10.1021/jacs.5b02254
05/2015
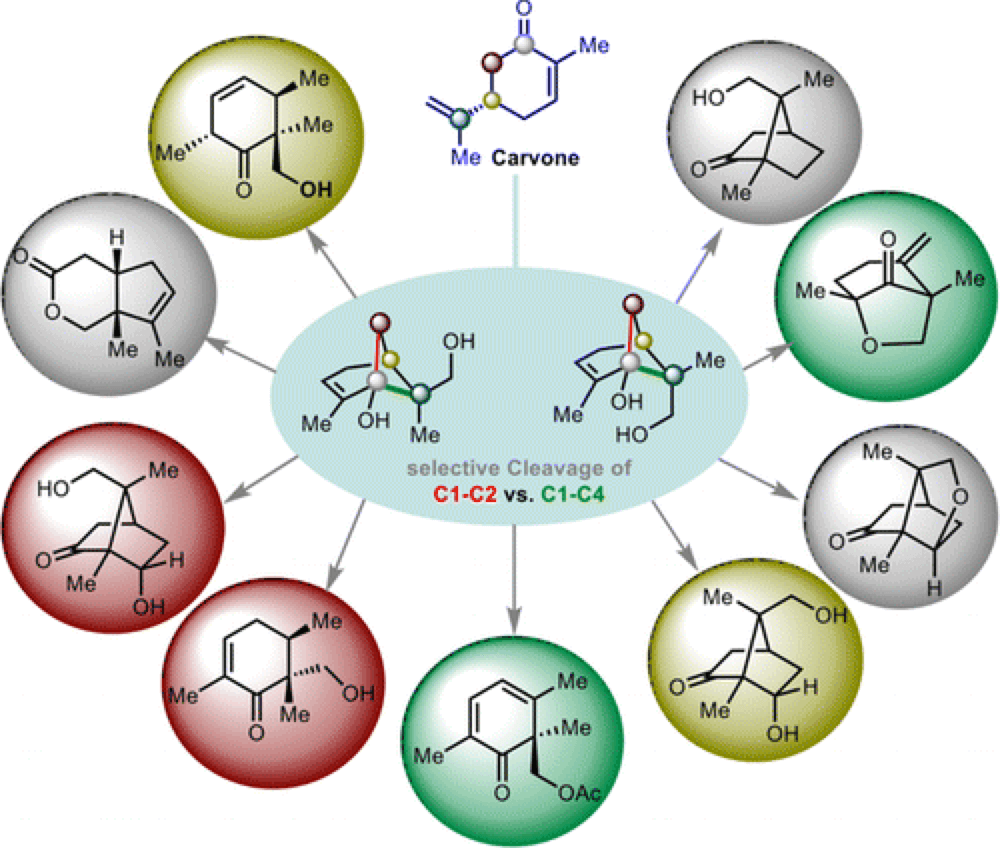
The continued development of transition-metal-mediated C–C bond activation/cleavage methods would provide even more opportunities to implement novel synthetic strategies. In this report the Sarpong Group have explored the Rh(I)-catalyzed C–C activation of cyclobutanols resident in hydroxylated derivatives of pinene, which proceed in a complementary manner to the C–C bond cleavage that we have observed with many traditional electrophilic reagents.
Mechanistic and computational studies have provided insight into the role of C–H bond activation in the stereochemical outcome of the Rh-catalyzed C–C bond activation process. Using this new approach, functionalized cyclohexenones that form the cores of natural products, including the spiroindicumides and phomactin A, have been accessed.