Palladium(0)/PAr3-Catalyzed Intermolecular Amination of C(sp3)–H Bonds: Synthesis of β-Amino Acids
Jian He, Toshihiko Shigenari, Jin-Quan Yu
Angew. Chem. Int. Ed.,
2015, 54, 22, 6454; 10.1002/anie.201502075
04/2015
Alkylated nitrogen-containing compounds are prevalent in biologically active compounds and widely used in modern drug discovery. The prevalence and importance of these compounds has driven the development of metal-catalyzed C–H Functionalization approaches to introducing nitrogen containing functionalities.
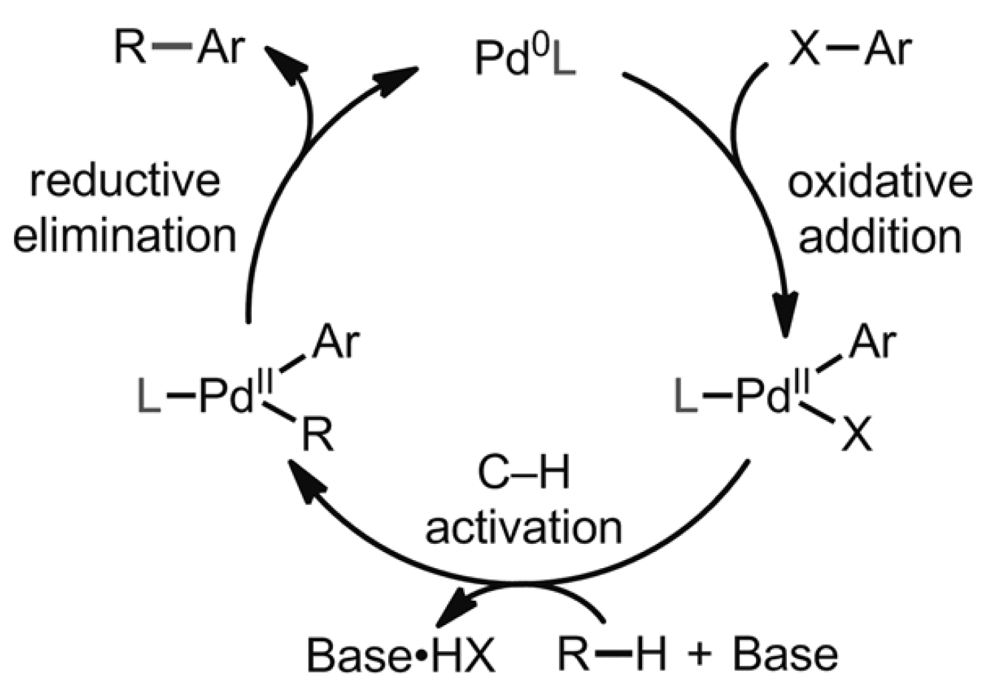
The Yu group report the first example of a Pd(0)/PAr3-catalyzed intermolecular amination of C(sp3)–H bonds in aliphatic amides, installing an alkylamine moiety at the beta-position. Recognizing that their recently developed work on Pd(0)-catalyzed intermolecular C(sp3)–H arylation and alkynylation reactions promoted by phosphine and N-heterocyclic carbene ligands could be applied to the use of amine coupling partners through an adjustment of the coupling partner provided a useful starting point.
Using N-oxime or N-chloro-amines a novel Pd(0)/Pd(II)-catalytic cycle to achieve intermolecular C(sp3)–H amination using an electron-deficient triarylphosphine ligand was achieved. The reaction was found to be general. The redox chemistry closely resembles Pd(0)-catalyzed C–H arylation with aryl halides and requires no general oxidants. This new technique provides access to novel beta-amino acids.