Copper-Catalyzed Oxidative Cyclization of Carboxylic Acids
Shyam Sathyamoorthi and J. Du Bois
Organic Letters,
2016, 18, (24), 6308-6311 DOI: 10.1021/acs.orglett.6b03176
12/2016
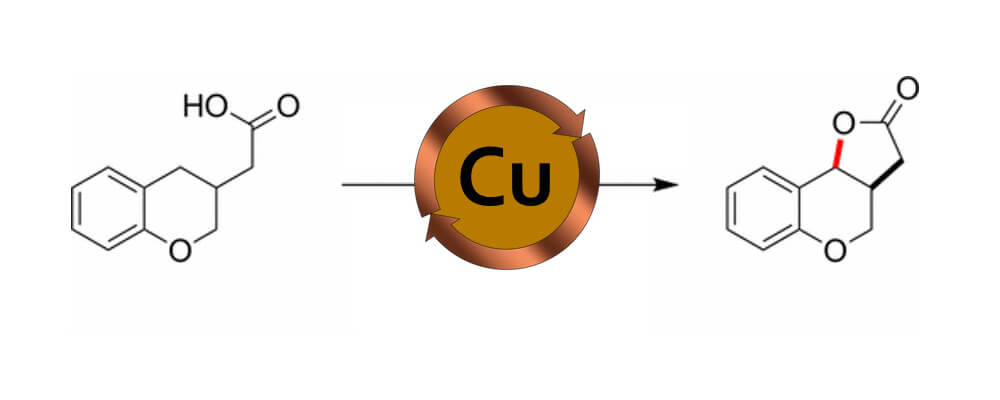
A method for converting C–H to C–O bonds through oxidative cyclization of carboxylic acids to generate lactone products is described. The reaction employs catalytic amounts of Cu(OAc)2 and potassium persulfate as the terminal oxidant and is performed open to air in an aqueous acetic acid solvent system. Preliminary mechanistic studies suggest that substrate oxidation likely proceeds by sulfate radical anion and that the Cu catalyst has no influence on the product-determining step. These conclusions differ from related investigations that propose the intermediacy of a carboxylate radical.